TI-83 Premium CE ou TI-82 Advanced
Syntaxe :
![]()
![]() [distrib]
[distrib] ![]() ...
...![]() A: binomFdp(
A: binomFdp(
![]()
![]() [distrib]
[distrib] ![]() ...
...![]() B: binomFRép(
B: binomFRép(
Les touches ![]()
![]()
![]() permettent d'ouvrir la fenêtre concernant les distributions.
permettent d'ouvrir la fenêtre concernant les distributions.
On descend ![]() jusqu'à A: binomFdp( ou B: binomFRép( pour accéder au calcul de probabilité.
jusqu'à A: binomFdp( ou B: binomFRép( pour accéder au calcul de probabilité.
Fondamental :
A: binomFdp( permet de calculer \(\mathsf{P(X}=x)\), \(x\) étant un entier positif.
Exemple : Réglages de la fenêtre
calcul de \(\mathsf{P(X}=5)\) avec \(\mathsf{X}\hookrightarrow \mathcal{B}(12 ;0,78)\)
nbreEssai : valeur de \(n\)
p : valeur de \(p\)
valeur de x : valeur de \(x\)
On positionne le curseur sur Coller et on appuie sur la touche ![]() .
.
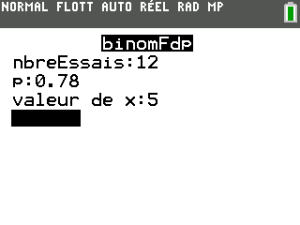
La calculatrice colle à l'écran la fonction avec les paramètres complétés : binomFdp(12 ,0.78,5) et on lance le calcul en tapant ![]() .
.
On obtient \(\mathsf{P(X}=5)\approx 0,0057\)
Fondamental :
B: binomFRep( permet de calculer \(\mathsf{P(X}\leqslant x)\), \(x\) étant un entier positif.
Exemple : Réglages de la fenêtre
calcul de \(\mathsf{P(X}\leqslant 5)\) avec \(\mathsf{X}\hookrightarrow \mathcal{B}(12 ;0,78)\)
nbreEssai : valeur de \(n\)
p : valeur de \(p\)
valeur de x : valeur de \(x\)
On positionne le curseur sur Coller et on appuie sur la touche ![]() .
.
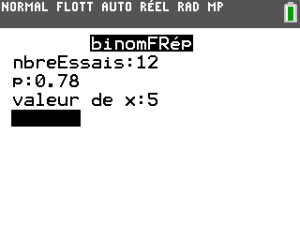
La calculatrice colle à l'écran la fonction avec les paramètres complétés : binomFRep(12 ,0.78,5) et on lance le calcul en tapant ![]() .
.
On obtient \(\mathsf{P(X}=5)\approx 0,0068\)